How NSX and SmartNICs (DPUs) accelerates the ESXi Hypervisor!
With vSphere 8 and NSX 4, VMware has introduced support for SmartNICs. SmartNICs are usually referred as DPUs (Data Processing Units). VMware has declared the DPU solution as Distributed Service Engine (DSE) under vSphere 8. There are several different names for the same function. In my blog post, I will primarily use the names DPU (Data Process Unit). The DPU-based acceleration for NSX emerged from the "Monterey" project, an initiative that was started by VMware about 2 years ago and has been steadily developed further.
The DPU architecture accelerates the networking and security function in the modern "Software Defined Data Center". NSX networking and security services are offloaded to DPUs to free up compute resources on the host. DPUs also provide enhanced visibility to show network communications. This helps with troubleshooting, mitigation against hacking attacks and compliance requirements. It enables VMware customers to run NSX services such as routing, switching, firewalling and monitoring directly on the DPU. This is particularly interesting for users who have significant demands in terms of high throughput, low latency and increased security standards.
ESXi SmartNICs Architecture
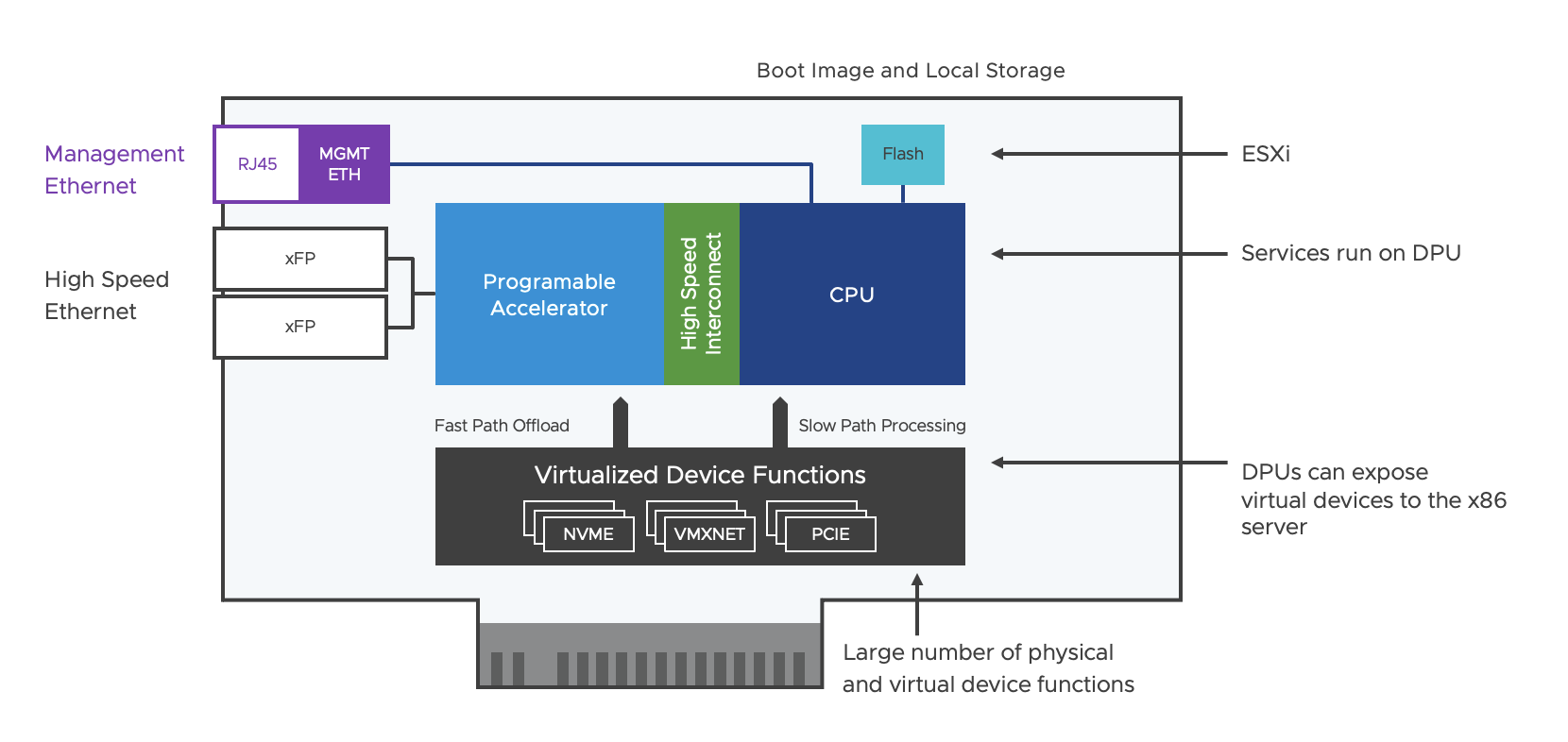
VMware relies on the ARM processor in the DPU Distributed Services Engine (DSE) solution with vSphere 8 and NSX 4 (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: SmartNICs Architecture
There is a local flash memory on the card to roll out the ESXi software via a boot image. A stripped-down version of ESXi is installed on the DPU, which is optimised for I/O requirements, such as packet offloading, external management, etc. For network connectivity, there are two Ethernet ports with SFP (small form-factor pluggable) modules and one RJ-45 copper port for a management connection. Configuration management runs independently of the x86 server and has been greatly simplified for operation. The Programmable Accelerator maps the packet processing function in hardware and ensures that data traffic is offloaded to the DPU and accelerated.
The High Speed Interconnect is the link between the Hardware Programmable Accelerator and the CPU, designed for low latency and high bandwidth.
Virtualised Device Functions (VDFs) enable network and storage devices to be provided as virtual devices. VDFs use Single Root I/O Virtualisation (SR-IOV) technology to connect virtual machines directly to physical devices, improving latency and throughput. They are able to combine the benefits of virtualisation with those of hardware acceleration. There is a one-to-one relationship between a VDF and a virtual machine (VM).
What are the advantages of DPU-based acceleration with NSX?
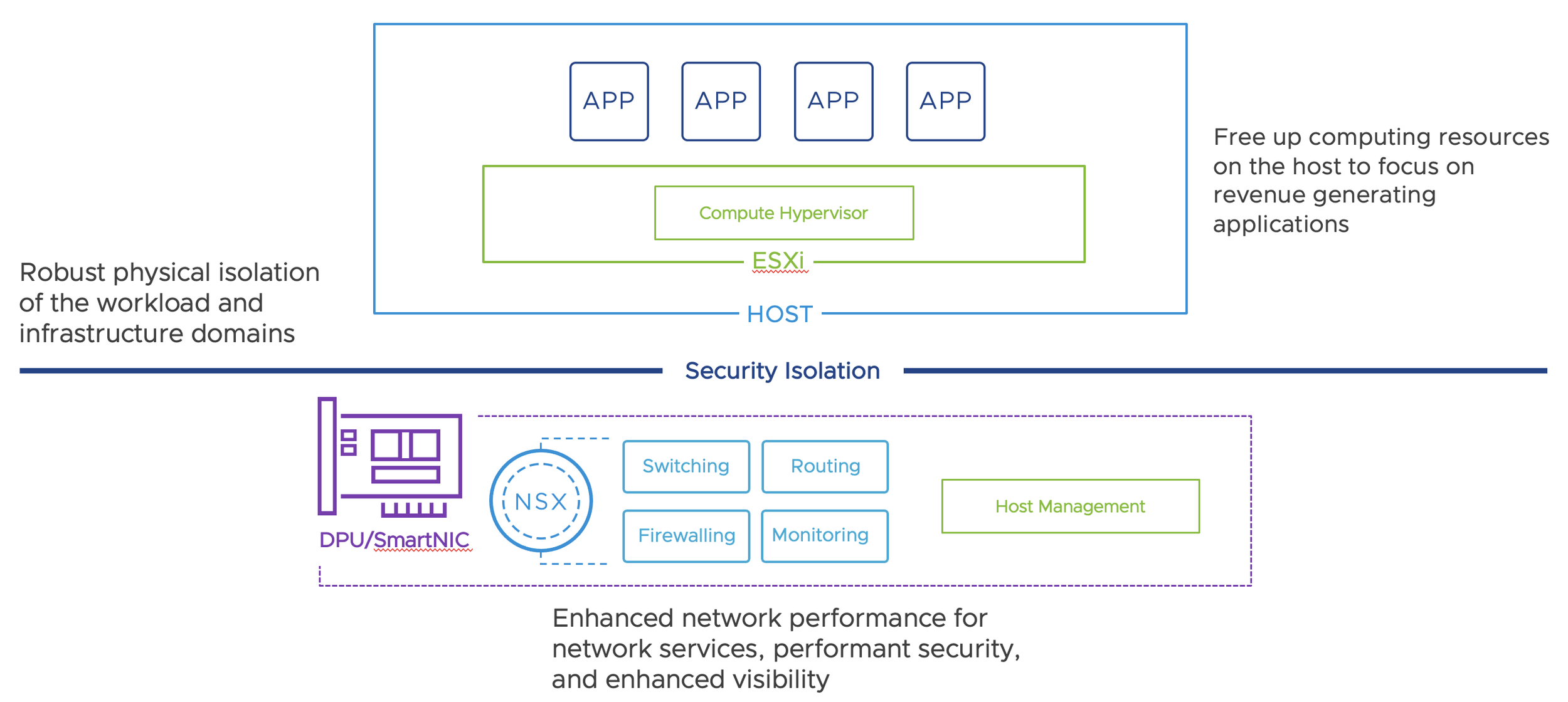
With SmartNICs, the NSX services (routing, switching, firewalling, monitoring) are outsourced from the hypervisor to the DPU (Data Process Unit), freeing up computing resources on the ESXi host for the applications (see Figure 2). An additional modified and specified ESXi image is installed on the DPU for this purpose. The new architecture runs the infrastructure services on the SmartNIC, providing the necessary separation between the application workloads running on the x86 computing platform and the infrastructure services. This is of enormous advantage for customers with high security and compliance requirements. Regulatory authorities such as the BSI (German Federal Office for Information Security) in particular often require separations of productive and management traffic for certain environments.
Figure 2: ESXi and SmartNICs
Advantages of DPU technology with NSX
1. Network performance optimization
DPUs are specifically designed for network services, overlay technology (such as VXLAN, GENEVE, etc.), load balancing, NAT (Network Address Translation) and therefore offer better performance than traditional generic CPUs. SmartNICs uses the VMDirectPath/UPTv2 (Uniform Passthrough) data path model with the advantage of passing traffic directly from the NIC to the virtual machine without a virtual switch.
2. Security
Security is one of the most important features of NSX. NSX Distributed Firewalling (Microsegmentation) uses a firewall engine on the ESXi hypervisor to roll out dedicated firewall rules directly to the virtual machines or containers. The NSX Distributed Firewall (DFW) acts in software and is completely independent of IP address ranges, each individual workload gets its dedicated firewall function and this from one management plane (NSX Manager). The DFW acts on layer 7, is stateful and does not require an agent for the ESXi hosts. NSX Intrusion Detection Prevention System (D-IDPS) uses technologies such as signature-based detection, behavioural analysis and machine learning to detect threats. NSX Distributed IDPS follows the same approach as NSX Distributed IDPS which means that the signatures are implemented directly in front of the dedicated workloads, also independently of IP ranges.
SmartNICs completely offload the security functions from the NSX DFW and NSX D-IDPS to the DPU. Running network security services on a DPU provides improved performance and granular security and monitoring of network traffic. This is particularly interesting for the IDPS function, as signatures are used to directly verify the payload of a packet, thereby placing a load on the CPU.
3. Visiblity
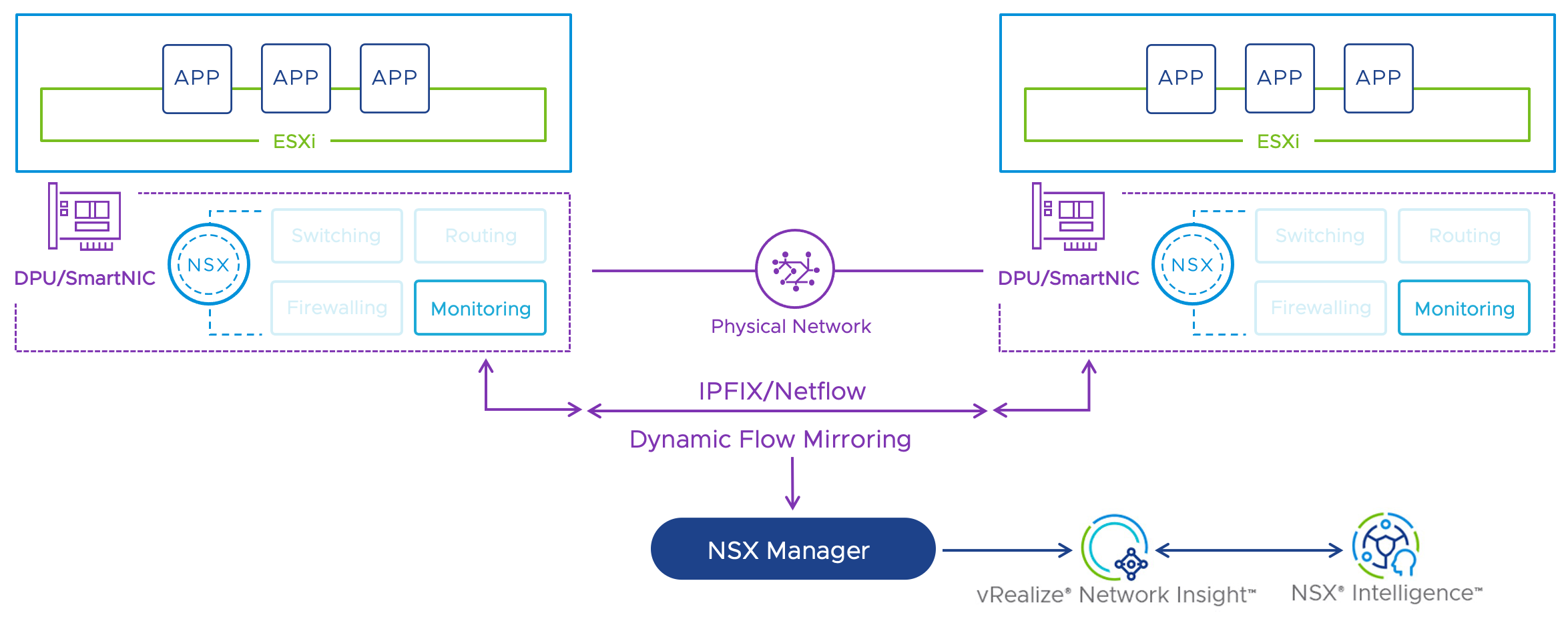
The DPU-based NSX solution can monitor all traffic flows directly on the network card. This means you can map full network visibility and observation, including advanced network topology views, flow and packet level capture and analysis, and IPFIX support (see figure 3). No complex port mirroring is required for this, such as so-called network TAPs or SPANs (Switch Port Analyzer).
Figure 3: Visibility with SmartNICs
Furthermore, because the network services running on DPUs are isolated from the ESXi components and applications, a DPU-based architecture facilitates the delineation of operational responsibilities between DevOps teams and VI administrators, who can focus on and manage host-level workloads, and NetSecOps teams, who can manage the network infrastructure and services on the SmartNIC.
4. Cost reduction
As mentioned earlier, by offloading networking and security services to the DPUs, more host resources are freed up for workloads. As a result, more workload capacity can be provided on fewer servers without compromising the monitoring, manageability and security features that vSphere and NSX provide.
You also benefit from operational savings by consolidating management across different workload types such as Kubernetes, containers and virtual machines, and simplifying the implementation of micro-segmentation, IDPS features and network monitoring without costly port mirroring.
5. Sustainability and energy savings
By increasing efficiency with SmartNICs, computing tasks are offloaded from the main processors, thereby reducing energy consumption and associated CO2 emissions.
As DPUs distribute power and efficiency to fewer servers, the number of hardware components required is reduced. This increases the lifetime of the devices and reduces the amount of waste, thus protecting the environment.
Which DPU functions are currently supported by VMware?
Currently, the network card manufacturers NVIDIA and Pensando (AMD) support the "Distributed Service Engine" DPU function of VMware with vSphere 8 and NSX 4. The DPU cards are supplied as a complete system by the server manufacturers Dell and HPE. Lenovo will also provide servers with DPUs in the future.
NSX version 4 supports the following DPU functions (Source: https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX/4.0.1.1/rn/vmware-nsx-4011-release-notes/index.html and https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX/4.1.0/rn/vmware-nsx-410-release-notes/index.html ):
Networking:
Overlay and VLAN based segments
Distributed IPv4 and IPv6 routing
NIC teaming across the SmartNIC / DPU ports
Security
Distributed Firewall
Distributed IDS/IPS (Tech Preview)
Visibility and Operations
Traceflow
IPFIX
Packet Capture
Port Mirroring
Statistics
Supported Vendors
NVIDIA Bluefield-2 (25Gb NIC models)
AMD / Pensando (25Gb and 100Gb NIC models)
Scale
Single DPU is supported per host consumed by single VDS
VMDirectPath (previous name UPTv2 - Uniform Passthrough): DPU-based Acceleration for NSX supports the ability to bypass the host level ESXi hypervisor and allow direct access to the DPU which allows customers to get high level of performance while not sacrificing the features that they leverage from vSphere and NSX.
SmartNIC support for Edge VM: DPDK vmxnet3 driver updates to support DPU-based (SmartNIC) pNICs for datapath interfaces on Edge VM form factor. Traffic through the Edge VM will benefit from this hardware acceleration. It can only be enabled on all datapath interfaces at the same time.
Summary:
Through SmartNICs with NSX 4 and vSphere 8, VMware improves speed at the hypervisor while taking into account the current network and security requirements of modern applications. Especially in times of increased security requirements due to ransomware and other potential attacks, this is an enormous advantage and the physical isolation of the workload and infrastructure domains as well. Purchases of new dedicated hardware in the form of additional DPU network cards with their own processors must be taken into account. This must be considered accordingly in future architecture planning. These investments are offset by savings in energy costs and a minimization of the total number of servers.